Visibility
Algorithm Description
Visibility (V) is the greatest horizontal distance at which selected objects can be seen and identified. Reduced visibility often occurs during periods of heavy rain and snow and also occurs when sunlight is scattered or absorbed by atmospheric particles. Fog droplets and haze particles are small enough to scatter and absorb sunlight, leading to reduced visibility. The visibility algorithm distinguishes between four visibility categories: clear (V 30 km), moderate (10 km V < 30 km), low (2 km V < 10 km), and poor (V < 2 km) visibilities. The clear sky (aerosol) visibility algorithm has a categorical success rate of 69%. The combined clear/cloud sky visibility retrieval has a categorical success rate of 64.5%. The visibility retrieval shows best performance during June-September where Heidke skill scores, which measures the fractional improvement relative to chance, are above 0.25. High biases in the clear sky (aerosol) component of the visibility algorithm can be reduced by applying a monthly bias correction using measurements from United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and National Park Service (NPS) Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environments (IMPROVE) network (Brunner et al, 2016). The IMPROVE network reports visibility using a deciview haze index (dV). Natural visibility conditions are approximately 10 dV in the eastern USA and 5 dV in the western USA.
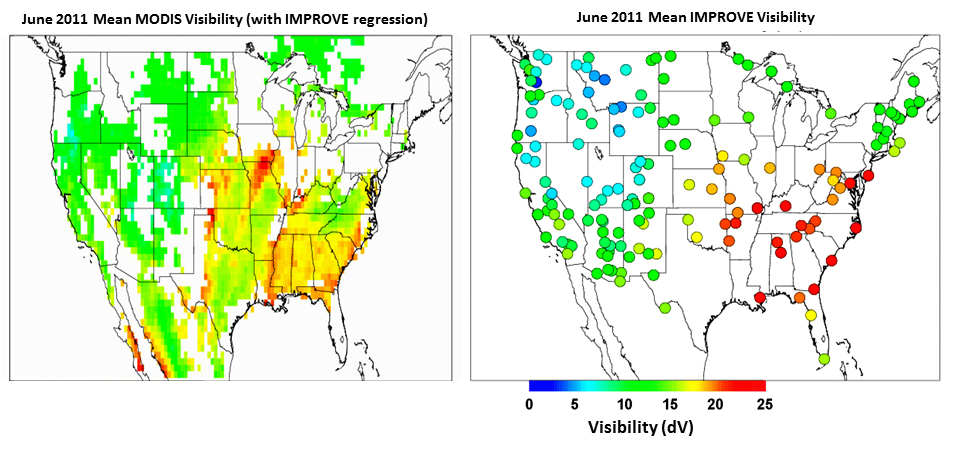
In the figure at right, Reduced visibility (higher dV) over the central and southeastern
US in June 2011 is associated with wildfires in the southwestern US and agricultural burning
in southern Georgia, northern Florida, and eastern North Carolina (Brunner et al., Development and validation of satellite-based
estimates of surface visibility, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 9, 409–422, 2016, DOI: 10.5194/amt-9-409-2016).
Main Applications
The Visibility retrieval provides a satellite based estimate of boundary layer slant range Visibility to augment existing measurements from surface networks. The ability to continuously monitor Visibility over the continental US allows smoke and fog related transportation hazards to be monitored in real time. In addition to these important safely considerations, reduced visibility due to regional haze also obscures the view in our nation’s parks. The Clean Air Act authorizes the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to protect visibility, or visual air quality, through a number of different programs, including the EPA’s Regional Haze Rule. The ability to continuously monitor Visibility in remote regions of the US will improve Visibility monitoring within our National Parks and provide useful information to the regional planning offices responsible for developing mitigation strategies required under the EPA’s Regional Haze Rule.
Key Users
The following NWP centers use some combination of the MODIS, VIIRS, and AVHRR polar winds in their operational systems. There are 13 NWP centers in 9 countries:
- Aviation Weather Center (AWC)
- National Weather Service (NWS)
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)
- Department of Transportation (DOT)
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Algorithm PI
Principal Investigator
R. Bradley Pierce
Operational Product Access
The visibility algorithm was developed for GOES-16 but is currently an option 2 product that is not produced operationally. Software to run the MODIS based aerosol visibility algorithm available through International MODIS/AIRS Processing Package (IMAPP)
Relevant External Links
List of satellite/instruments for algorithm
- Terra and Aqua MODIS