Laboratory for Satellite Altimetry / Sea Ice and Polar Dynamics Science Team
Validation Experiments: AAA 2006
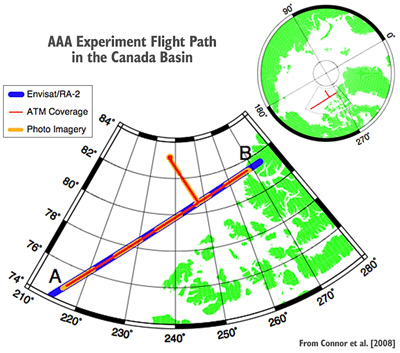
AAA Experiment Flight Path in the Canada Basin
The Arctic Aircraft Altimeter (AAA) 2006 campaign was carried out on March 27, 2006 to gather measurements of sea ice surface characteristics from multiple airborne instruments simultaneously with overpasses of the Envisat and ICESat satellites. Laser altimetry, D2P radar altimetry, and photography were collected by the NASA P3 aircraft along a 1300 km ground- track, to validate sea ice elevation measurements derived from the Envisat/RA-2 microwave altimeter and the ICESat laser altimeter. The experiment was conducted in the Canada Basin region of the Arctic Ocean as shown in the map below. Analysis showed good agreement between the satellite-derived sea ice elevations and those measured by the airborne laser altimeter (ATM), particularly over refrozen leads, where the overall mean difference was 1 cm. Further details of the Envisat validation can be found in Connor et al. [2008].
Significance: The AAA experiment provided a detailed independent airborne data set which was used to validate satellite altimetry measurements from Envisat and ICESat.
NASA was a partner while University College London (UCL) and the European Space Agency (ESA) were collaborators in this work.
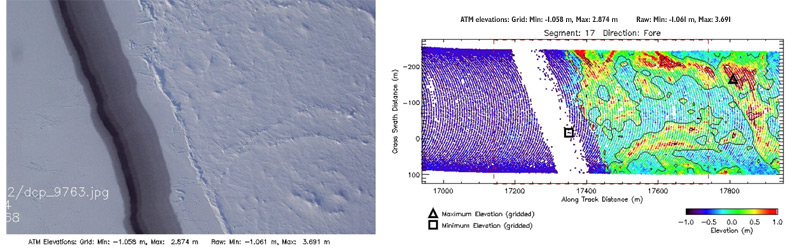
Comparison of nadir-looking photography (left) with elevation data (right) collected by the Airborne Topographic Mapper (ATM) system. A lead (dark linear feature in photography) is identified in the elevation as the lowest elevation measured.



