GOES-14 Captures Detailed Imagery of the December East Coast Blizzard
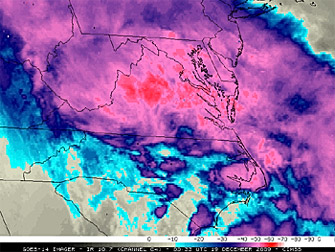
Above: GOES-14 10.7 µm IR channel image
Below: Visible imager view of December 19 cloud cover
21 December 2009 - An intense winter
storm impacted a large portion of the mid-Atlantic and Northeast regions
of the US on 18 December - 19 December 2009, creating blizzard conditions
and setting a number of snowfall records. As a part of its ongoing NOAA Science
Test, the GOES-14 satellite was placed into Super Rapid Scan
Operations (SRSO) mode, supplying imagery at 1-minute intervals during
much of the storm life cycle. McIDAS images of the GOES-14 10.7 µm
IR channel data showed the formation of a large, cold cloud shield early
in the period, followed by the development of a number of convective bands
after about 03:00 UTC on 19 December which then helped to further enhance
snowfall rates.
According to STAR's Tim Schmit, the GOES-14 Science
test allows the unique opportunity for a longer running collect of
information in the super rapid scan mode. With the operational satellites,
such a scan is usually run for just a few hours.
More Info
Special thanks Scott Bachmeier of CIMSS for creating the GOES-14 IR
imagery animation from the storm and Dan Lindsey for the visible loop. The
GOES-14 Science Test is co-lead by Tim Schmit and Don Hillger, both of
STAR.
NOAA-led GOES-14 Science Test Underway
9 December 2009 - The GOES-14 science test has
begun, lead by scientists from STAR. It runs until January 4th. This
period allows for special scanning scenarios for both the GOES-14 Imager
and the Sounder.
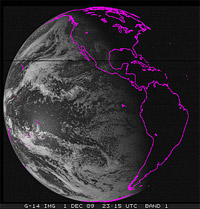
GOES-14 Earth Imager Band 1 - Visible - 12-1-2009
(4MB animation)
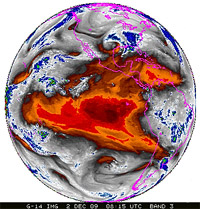
GOES-14 Earth Imager Band 3 - Water Vapor - 12-1-2009
(2.3MB animation)
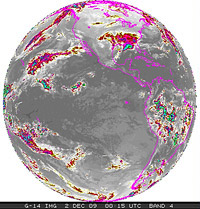
GOES-14 Earth Imager Band 4 - Long Wave IR - 12-1-2009
(2.4MB animation)
For all GOES check-outs, the goals of the Science Test include the following:
- To assess the quality of the GOES radiance data. This is
accomplished by comparison to other satellite measurements or by
calculating the signal-to-noise ratio compared to specifications, as
well as assess the striping in the imagery due to multiple
detectors.
- To generate products from the GOES data stream and compare to those
produced from other satellites. These included several Imager and
Sounder products currently used in operations.
- Rapid-scan imagery of interesting weather cases are collected with
temporal resolutions as fine as every 30 seconds, a capability of
rapid-scan imagery from GOES-R that is not implemented operationally on
current GOES.
More details on the GOES-14 Science Test can be found at: http://rammb.cira.colostate.edu/projects/goes-o/.
GOES-14 First IR Images On-Line
August 17, 2009 - The first full-disk infrared (IR)
image from GOES-14, captured on 17 August 2009 at 1730 UTC, are shown. This
will be followed by the first IR images from the Sounder. Testing of the
spacecraft and its instruments will continue through the entire Post
Launch Test (PLT) period.
Click each of the images below to view a larger version.
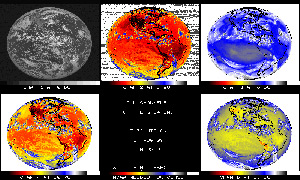
GOES-14 Imager Infrared Earth Image -
All Bands in Color (6 panels) -
August 17, 2009
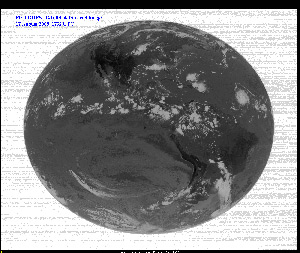
First GOES-14 Full Disk Infrared Image -
August 17, 2009 - IR2
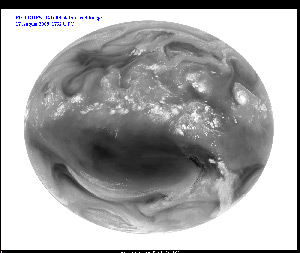
First GOES-14 Full Disk Infrared Image -
August 17, 2009 - IR3
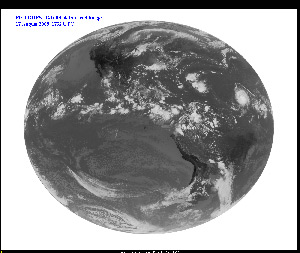
First GOES-14 Full Disk Infrared Image -
August 17, 2009 - IR4
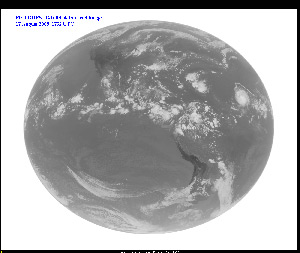
First GOES-14 Full Disk Infrared Image -
August 17, 2009 - IR6
STAR is leading the GOES-14 Science Test. Participants include scientists
both inside and outside of NOAA, and from STAR, Tim Schmit and Don
Hillger, among others. The results of the Science Test will be available
on the GOES-14 Science Test page,
and when finished, a NOAA Technical Report with Science Test findings will be published. Images
of the IR bands have been posted at: http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/media/spotlight/goes14/ir.html.
The GOES (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) series of
U.S. satellites are developed by a joint NASA-NOAA-Industry partnership,
launched by NASA (with industry partners), and operated by NOAA.
Comparison: GOES-14 Sounder vs. GOES-12 Sounder
Click each of the images below to view a larger version.
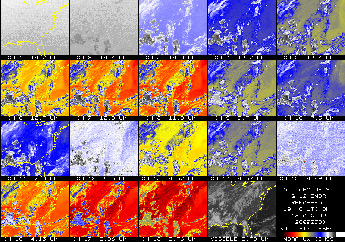
GOES-12 Sounder Channels 1-18 comparison image -
August 18, 2009
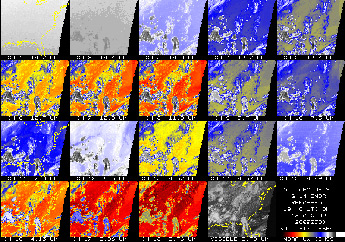
GOES-14 Sounder Channels 1-18 comparison image - August 18, 2009
August 18, 2009 - Note the much cleaner signal to
noise ratio on the GOES-14 Sounder (compared to the GOES-12 sounder). This
is especially evident in sounder bands 1, 2, 12 and 15. A 'Sounder' is
used to estimate temperature and moisture profiles in the atmosphere. It
can also derived information on clouds and certain trace gases.
STAR News - GOES-14 First Image &
STAR's Lead Role in the NOAA Science Test
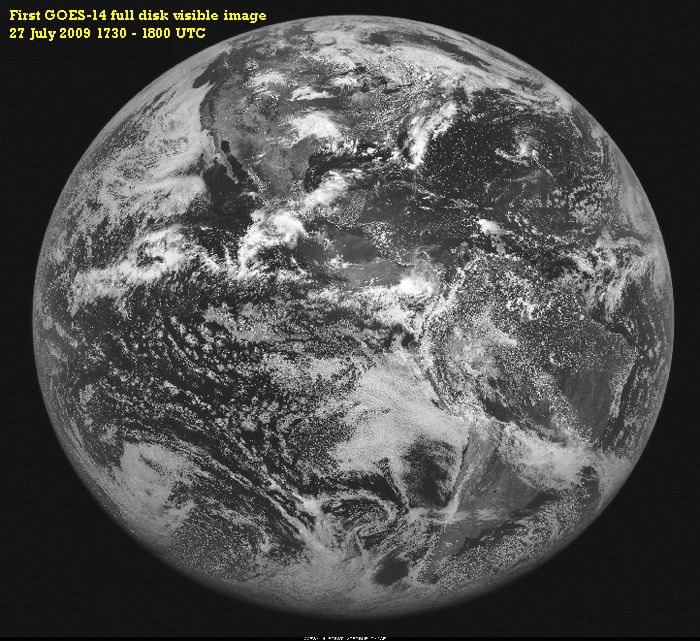
First GOES-14 Full Disk Image, July 27, 2009 1730-1800 UTC
Click image above to view full size image (2300 x 1900 pixels, 2.8MB)
July 27, 2009 - GOES-O was launched on 28 June 2009 and has successfully reached
geostationary orbit to become GOES-14, the latest in the long line of GOES
which started with the SMS/GOES program in the mid-1970s. GOES-14 is the
second in the current GOES series, after which there will be one more
launch, GOES-P, to be followed by the next generation GOES-R in 2015.
The first full-disk visible image from GOES-14, captured on 27 July
2009 at 1730 UTC, is shown. This will be followed by the first IR images
and then Sounder data. Testing of the spacecraft and its instruments will
continue through the entire Post Launch Test (PLT) period. The last part
of that PLT period will be the NOAA Science Test, during which the
satellite instrumentation will be controlled to provide special data. The
Science Test is currently scheduled for December 2009. Operational
scenarios and special imagery will be collected, to test both Imager and
Sounder characteristics and the generation of products from the GOES-14
data stream.
STAR is leading the GOES-14 Science Test. Participants include
scientists both inside and outside of NOAA. The results of the Science
Test will be available on the GOES-14
Science Test page, and when finished, a NOAA Technical Report with
Science Test findings will be published. Any scientists not already
participating but interested in the Science Test data should contact
either Don Hillger (STAR/RAMMB) or Tim Schmit (STAR/ASPB).
The GOES (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) series of
U.S. satellites are developed by a joint NASA-NOAA-Industry partnership,
launched by NASA (with industry partners), and operated by NOAA.



