Ocean Topography and Cryosphere Branch / Laboratory for Satellite Altimetry / Sea Level Rise
Products / tide gauge comparison
Tide gauges used for altimeter comparisons
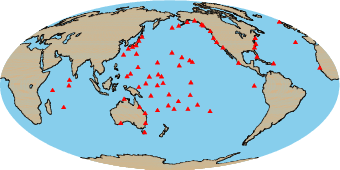
The method of producing estimates of altimeter drift using a global network of tide gauges is described in detail by Mitchum (2000). Briefly, the method works by creating an altimetric time series at a tide gauge location, and then differencing this time series with the tide gauge sea level time series. In this difference series, ocean signals common to both series largely cancel, leaving a time series that is dominated by the sum of the altimetric drift and the land motion at the tide gauge site. Making separate estimates of the land motion rates and combining the difference series from a large number of gauges globally results in a times series that is dominated by the altimeter drift. Since the difference series at separate time gauge locations have been shown to be nearly statistically independent (Mitchum, 1998), the final drift series has a variance much smaller than any of the individual series that go into it. Because of the relatively large number of degrees of freedom, this method outperforms comparisons from dedicated calibration sites, although it is only a relative comparison, meaning that it cannot determine any absolute bias. It can, however, detect change in a bias, either a drift or a step change.
Tide gauge comparison results |
|---|
Comparison of TOPEX/Jason-1/Jason-2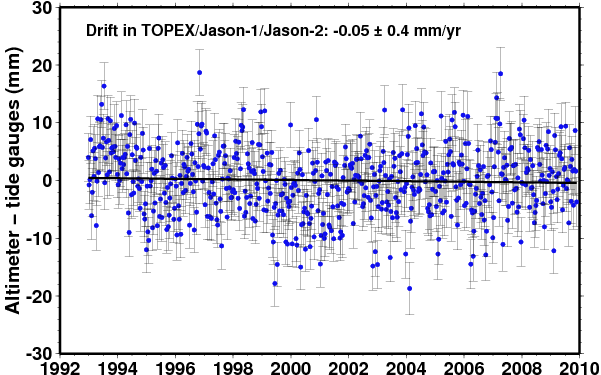 |
Comparison of TOPEX/Poseidon original mission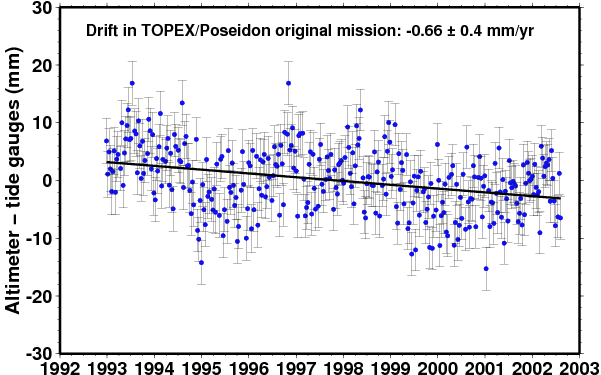 |
Comparison of TOPEX/Poseidon interleaved mission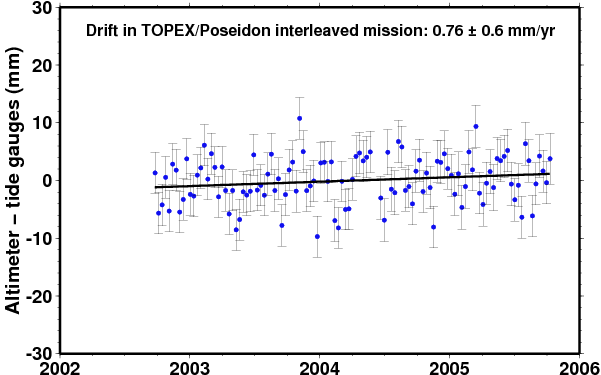 |
Comparison of Jason-1 original mission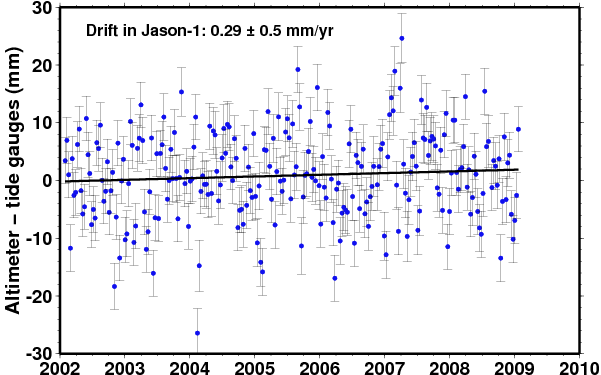 |
Comparison of Jason-2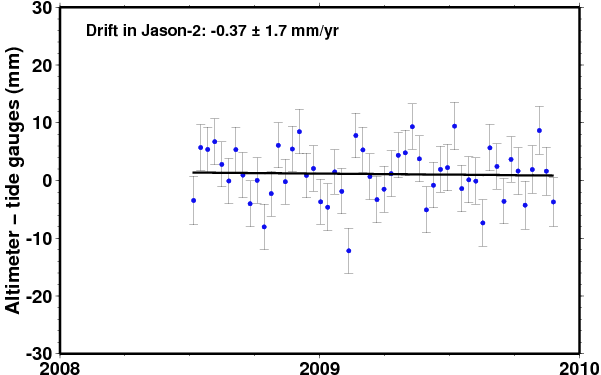 |
Comparison of Envisat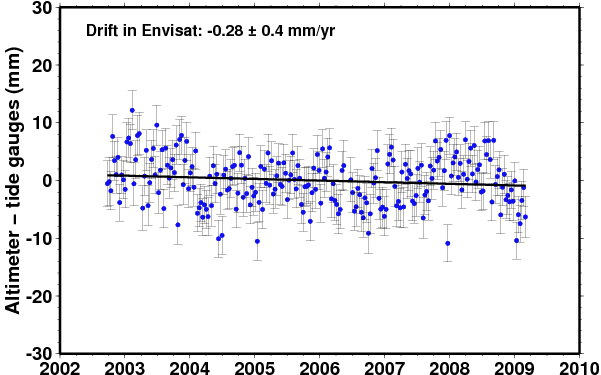 |
Comparison of ERS-2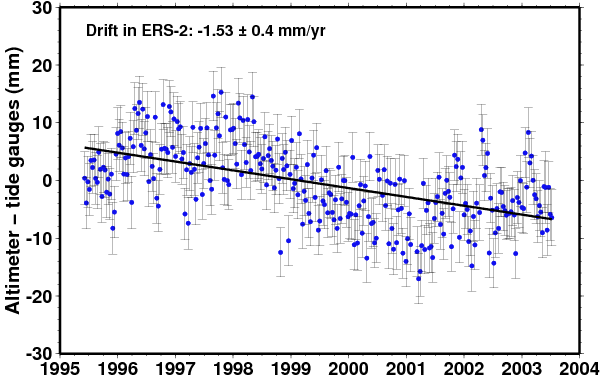 |
