Sensors
WindSat Overview
Satellite(s)
Coriolis
MiRS Production Status
Experimental / research
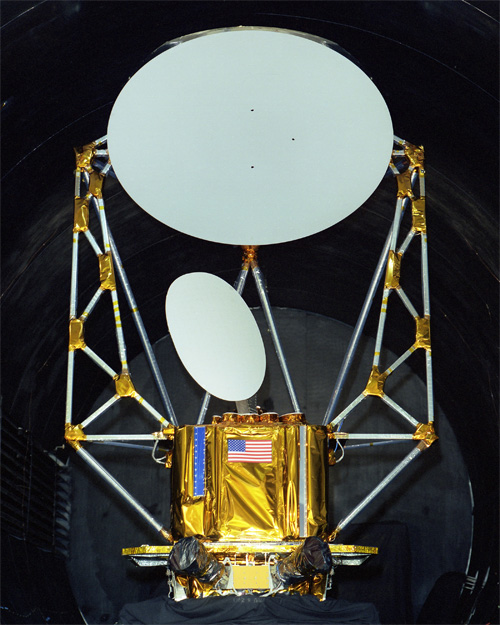
WINDSAT is a joint IPO/DoD/NASA risk reduction demonstration project intended to measure ocean surface wind speed and wind direction from space using a polarimetric radiometer.
WindSat is a polarimetric microwave radiometer developed by the U.S. Navy and the National Polar-orbiting Operational Enviromental Satellite System (NPOESS) Integrated Program Office (IPO) for measuring ocean surface wind speed and direction. WindSat will demonstrate the viability of using polarimetry to measure the wind vector from space and provide operationally usable tactical information to Navy units. The payload provides risk reduction data that the NPOESS IPO will use in the development of the Conical Microwave Imager Sounder (CMIS). WindSat is the primary payload on the DoD Space Test Program's Coriolis Mission.
The WindSat payload is a multi-frequency polarimetric radiometer nominally operating at 6.8, 10.7, 18.7, 23.8, and 37 GHz. Using a conically-scanned 1.83 m offset parabolic reflector with multiple feeds, WindSat will cover a 1025 km active swath (based on an altitude of 830 km) and provide both fore and aft views of the swath. The horizontal ground resolution is determined by the size of the antenna and the altitude. The relatively large WindSat antenna will result in spatial resolutions approximately three times greater than current systems, improving the utility of the imagery data and enabling better measurements in the littoral. The 10.7, 18.7, and 37.0 GHz channels are fully polarimetric; that is, they derive all four Stokes parameters by measuring the six principal polarizations. The 6.8 GHz channel is dual polarimetric (vertical and horizontal) and provides sea surface temperature as a secondary product. The 23.8 GHz channel is also dual polarimetric because its purpose is to correct for atmospheric water vapor which is unpolarized.
The radiometer operates in discrete bands at 6.8, 10.7, 18.7, 23.8, and 37.0 GHz. Table 1 provides key design and performance parameters of the system. The 10.7, 18.7, and 37.0 GHz channels are fully polarimetric. The 6.8 channel is dual-polarization (vertical and horizontal), and is more sensitive to sea surface temperature (SST) than to winds. Thus it is used to remove measurement noise due to variations in SST. Similarly, the 23.8 channel has dual-polarization. This frequency responds strongly to water vapor in the atmosphere, which attenuates the signal from the ocean surface. Thus, 23.8 channel data mitigates the effects of the water vapor.
| Freq(GHz) | Channels | Band Width(MHz) | τ(ms) | NE∆T(1) | Earth Incidence Angle (deg) |
IFOV(km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.8 | V,H | 125 | 5.00 | 0.48 | 53.5 | 40X60 |
| 10.7 | V,H ±45,L, R | 300 | 3.50 | 0.37 | 49.9 | 25X38 |
| 18.7 | V,H ±45,L, R | 750 | 2.00 | 0.39 | 55.3 | 16X27 |
| 23.8 | V,H | 500 | 1.48 | 0.55 | 53.0 | 12X20 |
| 37.0 | V,H ±45,L, R | 2000 | 1.00 | 0.45 | 53.0 | 8X13 |
Notes:
- V : Polarization vector is parallel to scan plane at nadir
- H : Polarization vector is perpendicular to scan plane at nadir
- ±45 : Linear Polarization
- L: Left Circular Polarization
- R: Right Circular Polarization
Source: NRL: WindSat - Remote Sensing of Ocean Surface Winds