STAR - Global Vegetation Health Products : Resource
Resource Information
Images presented in this section provide additional information useful for analysis and interpretation of Vegetation Health data and products.
Long term maps include: Ecosystems, Desert map,
Elevation
Real-time maps include: Snow/Ice map
and Rainfall from Hydro-Estimator and
CMORPH products.
Ecosystems
Ecosystems map is based on USGS "Global Land Cover Characteristics Data Base (GLCC World )"
at a 30 arc second resolution using 17 clutter categories.
URL:
http://www.pathloss.com/pwiki/index.php?title=Global_Land_Cover_Characteristics_Data_Base_(GLCC_World)
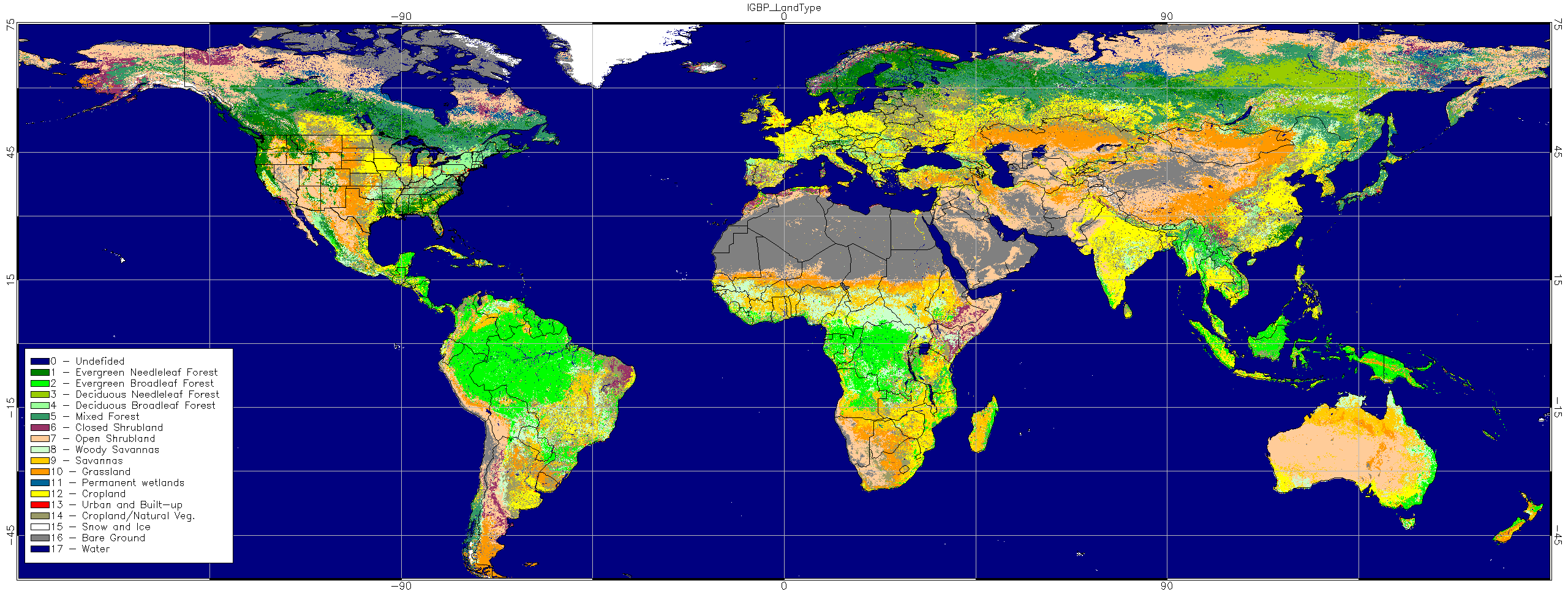
|
0 - Undefined 1 - Evergreen Needleleaf Forest 2 - Evergreen Broadleaf Forest 3 - Deciduous Needleleaf Forest 4 - Deciduous Broadleaf Forest 5 - Mixed Forest |
6 - Closed Shrubland 7 - Open Shrubland 8 - Woody Savannas 9 - Savannas 10 - Grassland 11 - Permanent wetlands |
12 - Cropland 13 - Urban and Built-up 14 - Cropland/Natural Veg. 15 - Snow and Ice 16 - Bare Ground 17 - Water Bodies |
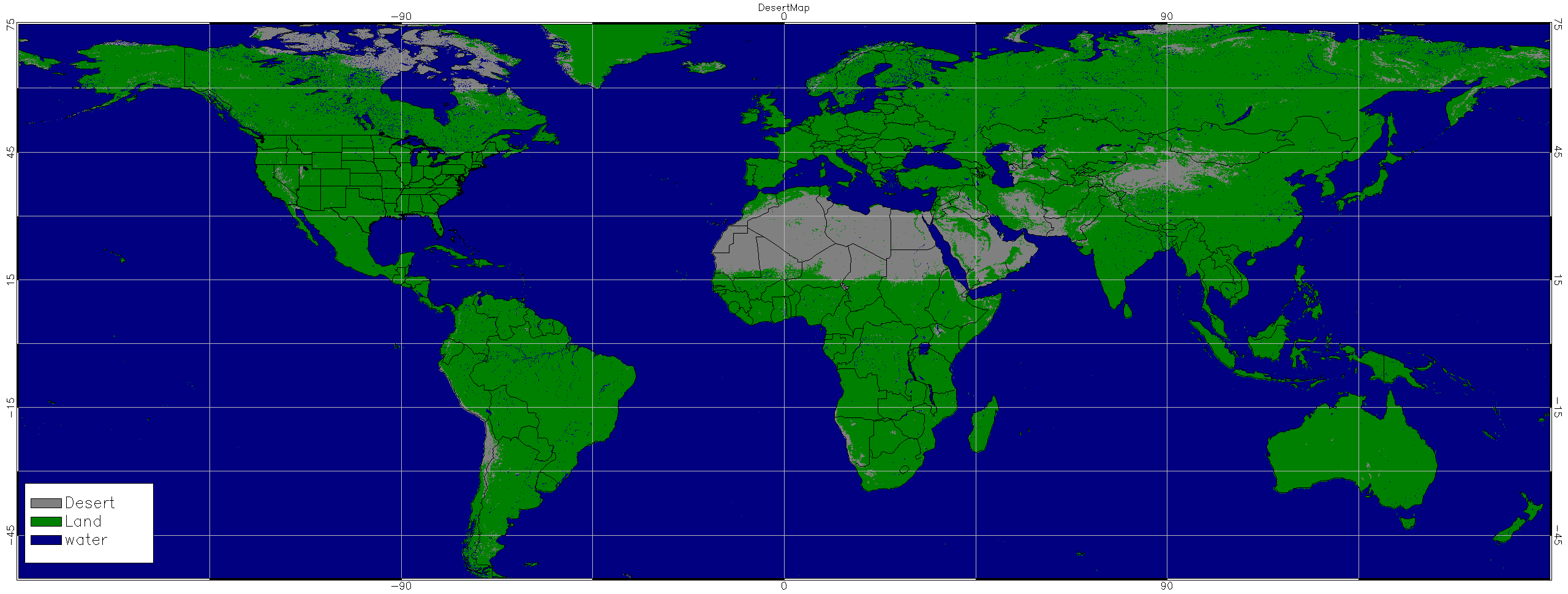
Desert map
Currently we use the class 16 (bare Ground) of USGS "Global Land
Cover Characteristics Data Base (GLCC World)" as desert mask. (see
above)
URL: http://www.pathloss.com/pwiki/index.php?title=Global_Land_Cover_Characteristics_Data_Base_(GLCC_World)
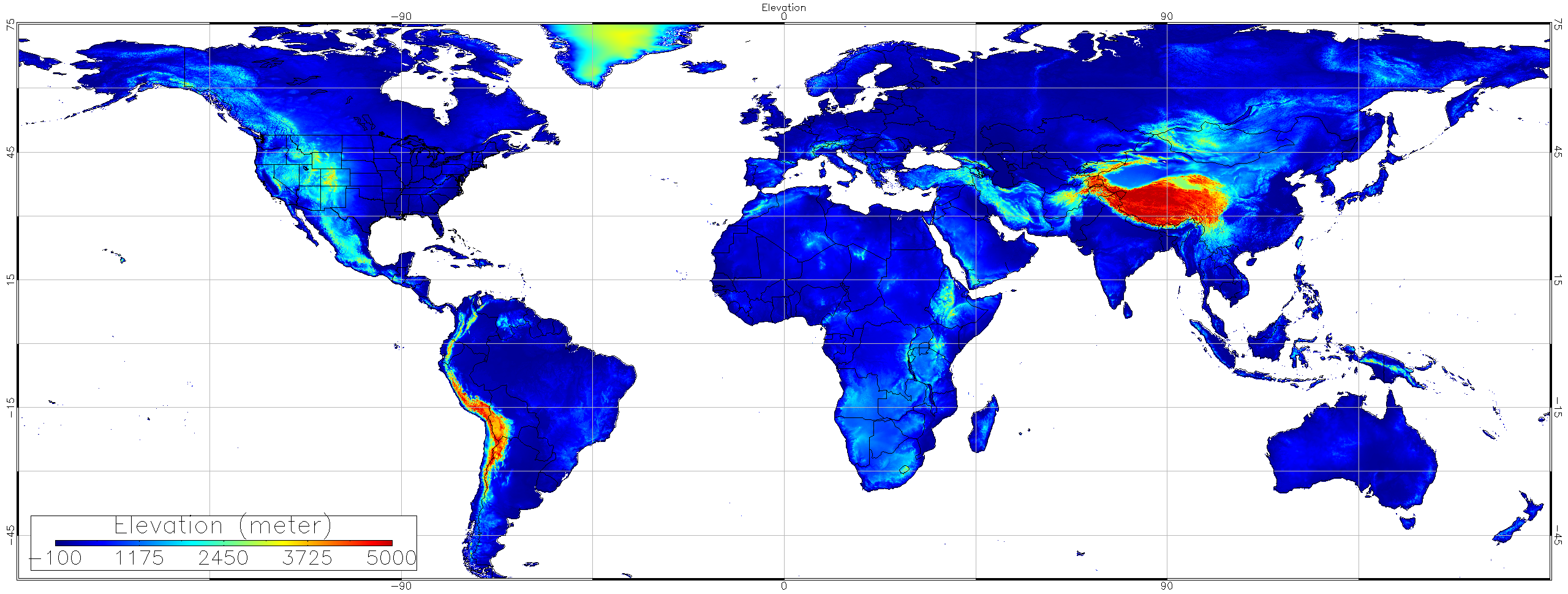
Elevation
Elevation data are obtained from NOAA National Geographical Data Center (NGDC) Global Land One-km Base Elevation Project (GLOBE) database at a 30-arc-second (1-km) gridded, quality-controlled global Digital Elevation Model (DEM).
GLOBE Task Team and
others (Hastings, David A., Paula K. Dunbar, Gerald M. Elphingstone,
Mark Bootz, Hiroshi Murakami, Hiroshi Maruyama, Hiroshi Masaharu, Peter
Holland, John Payne, Nevin A. Bryant, Thomas L. Logan, J.-P. Muller,
Gunter Schreier, and John S. MacDonald), eds., 1999. The Global Land
One-kilometer Base Elevation (GLOBE) Digital Elevation Model, Version
1.0. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National
Geophysical Data Center, 325 Broadway, Boulder, Colorado 80305-3328,
U.S.A. Digital data base on the World Wide Web (URL: http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/topo/globe.html) and CD-ROMs.
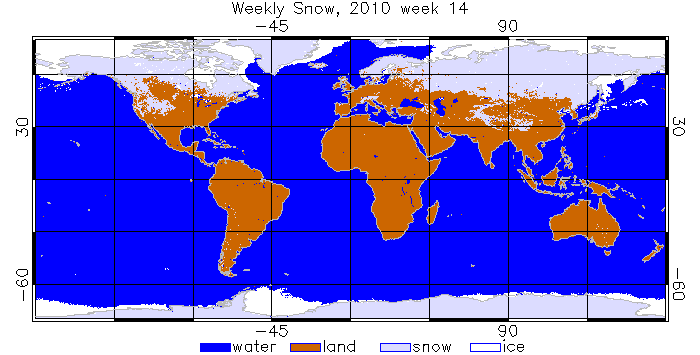
Snow/Ice
Global Multisensor Snow/Ice Cover Map is derived from combined observations of NOAA AVHRR, MSG SEVIRI, GOES Imager and DMSP SSM/I. The algorithm is fully automated. It is an experimental product which data has been available since Jan 1, 2006.
URL: https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/smcd/emb/snow/HTML/multisensor_global_snow_ice.html
We aggregated daily snow data to weekly map. Below is an example:
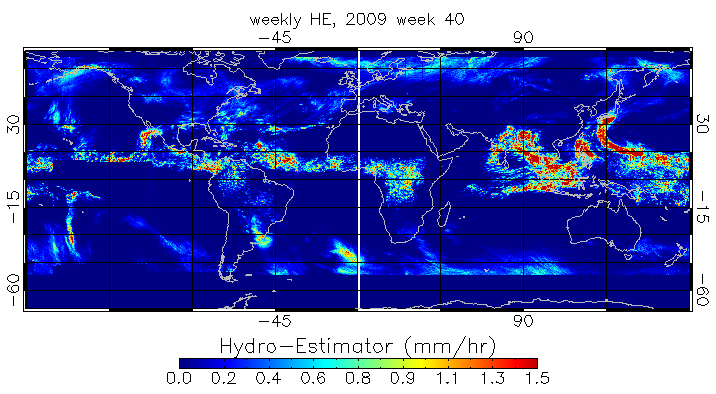
Rainfall: Hydro-Estimator (H-E)
Hydro-Estimator (H-E) is NOAA NESDIS STAR Satellite Rainfall Estimates product.
URL: https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/smcd/emb/ff/HydroEst.php
The H-E is based on brightness temperature measurements in the IR window (~11 µm) observed by the five geostationary satellites (GOES-11 and -12 over the Western Hemisphere, METEOSAT-9 over Europe and Africa, METEOSAT-7 over central Asia and the Indian Ocean, and Multi-Functional Transport Satellite (MTSAT)-1 over eastern Asia, Australia, and the Western Pacific Ocean). (Scofield and Kuligowski 2003)
Global H-E data was in resolution of 0.04438 degree and available hourly since 2008. We aggregated hourly H-E data to weekly accumulative precipitation. Below is an example of weekly weekly rainfall image derived from H-E:
Rainfall: CMORPH product
CMORPH product
was obtained from NOAA Climate Prediction Center (CPC).
URL: http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/janowiak/cmorph_description.html
CMORPH (CPC MORPHing technique) produces global precipitation analyses at very high spatial and temporal resolution. This technique uses precipitation estimates that have been derived from low orbiter satellite microwave observations exclusively, and whose features are transported via spatial propagation information that is obtained entirely from geostationary satellite IR data. At present we incorporate precipitation estimates derived from the passive microwaves aboard the DMSP 13, 14 & 15 (SSM/I), the NOAA-15, 16, 17 & 18 (AMSU-B), and AMSR-E and TMI aboard NASA's Aqua and TRMM spacecraft, respectively.
The global 3 hourly CMORPH rain rate data with 0.25 degree resolution
were aggregated to weekly accumulative precipitation.
Below is an example of weekly rainfall image derived from CMORPH: